Cervical Spondylosis
Best Cervical Spondylosis Treatment in Mumbai
Cervical Spondylosis Meaning:
Cervical Spondylosis or Cervical Spondylitis means arthritis of cervical vertebral joints (disc and facets). The cause of pain in cervical spondylosis is similar to knee arthritis. As disc degenerates, it loses its capability as shock absorber. Similarly, facet joints get rough due to loss of smooth cartilage on its surface. These factors cause significant friction between adjacent bone surfaces leading to pain in the local area. Most of the times, cervical spondylosis is accompanied by cervical disc prolapse and cervical spinal stenosis of varying degrees. Primary cause of cervical spondylosis is age related degeneration (chronic wear and tear) of disc and facet joints. It primarily affects elderly patients. Obese individuals and people with poor lifestyle (wrong posture, computer work, excessive phone use) are more prone to develop these degenerative changes. Occasionally, acute injury and accident also can lead to spondylosis at a younger age.
Cervical Spondylosis Symptoms:
Typical symptoms of cervical spondylosis is pain in the neck. Pain may also radiates to nearby areas like shoulder and arm. If there is associated disc prolapse or spinal canal stenosis, patient may also have neurological symptoms (pain in arms, tingling-numbness, loss of sensation, weakness etc.).
Cervical Spondylosis Diagnosis:
Cervical Spondylosis is primarily diagnosed by history of local pain in spinal area. In addition following tests can be done:
- X-ray: An x-ray will show loss of disc height, indicating thinning of disc material. An x-ray in different positions (flexion-extension) will reveal any associated spinal instability, which might be missed on static imaging, like MRI.
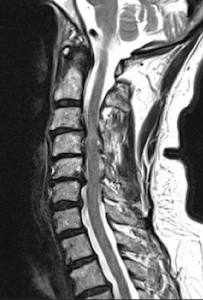
- MRI Scan: It will show loss of water content of disc material (disc desiccation), arthritis of facet joints and associated spinal stenosis.
- CT Scan: to assess bony anatomy in detail.
- Other tests, like EMG-NCV, blood tests etc, might be required to confirm or rule out any associated pathology.
Cervical Spondylosis Treatment:
- Medical Treatment: Like any other spine condition, initial treatment of cervical spondylosis is primarily by medicines, local heat/ ice, bracing, activity restriction and physiotherapy. Physiotherapy helps build muscle strength and relieves muscle spasm. Stronger muscle will act as internal brace and will prevent excessive motion at painful spinal segment.
- Cervical Spondylosis Exercises/ Cervical Spondylosis Physiotherapy: Neck muscle strengthening and range of motion (ROM) are usually prescribed to the patient to strengthen their neck muscles. This in turn support the spine better and reduces neck pain. These exercises also reduce neck muscle spasm, which is a common source of neck pain due to cervical spondylosis. Physiotherapists also use certain modalities (e.g. IFT, Ultrasound, Cupping etc.) as pain management for cervical spondylosis symptoms.
- Pain Management: There are various procedures targeting facet joint (facet injection, Radio-Frequency nerve ablation) or the spinal cord (root block, epidural injection). These procedures are done to provide pain relief. They do not reverse degenerative changes in spine.
Cervical Spondylosis Surgery:
- Spine Fusion/ Instrumentation Surgery: Primary reason of pain in spondylosis is friction of arthritic surfaces. Spine instrumentation aims at eliminating this painful motion. Bone fusion is usually done along with spine instrumentation for long term success of the surgery. Most of the spine fusion surgeries can be done now with minimally invasive/ key-hole techniques. A decompression procedure is usually done simultaneously with spine fusion surgeries. Extent of spine decompress in will depend on amount of spinal stenosis.
- Disc Replacement Surgery: One of the drawback of spine fusion surgery is loss of movements at operated level. This leads to certain movement restrictions to the patients. Also, after spine fusion there is increased stress on adjacent vertebral motion segments due to distribution of lost movements at operated level. This might lead to accelerated degeneration of adjacent disc/ facet joints (called Adjacent Segment Degeneration in medical terms). To prevent these, disc replacement can be done which maintains movements at operated level also. Cervical disc replacement surgery gives good results in a carefully selected patient young patient who have only disc degeneration with normal facet joints. As only disc is replaced in disc replacement surgery, if there is associated facet arthritis, pain relief will not be adequate as pain from facet joints will persist. For patients with advanced arthritis, spine fusion will give more predictive results.
Differential Diagnosis of Cervical Spondylosis:
Cervical spondylosis is a condition that affects the joints and discs of the neck, causing pain and stiffness. It is a common condition among older adults, and it can affect their quality of life. However, the symptoms of cervical spondylosis can be similar to other conditions, which makes it challenging to diagnose. This is where the importance of differential diagnosis comes into play.
Differential diagnosis is a process used by healthcare professionals to rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. In the case of cervical spondylosis, the symptoms may be similar to those of other conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and osteoarthritis. Therefore, it is essential to differentiate between these conditions to provide the appropriate treatment.
The process of differential diagnosis involves a thorough examination of the patient’s medical history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests. The medical history includes information about the patient’s symptoms, any previous injuries or surgeries, and any medications they may be taking. The physical exam involves assessing the patient’s range of motion, muscle strength, and any tender points in the neck.
The diagnostic tests used to differentiate between cervical spondylosis and other conditions include X-rays, CT scans, and MRI. These tests allow healthcare professionals to visualize the spine and assess the severity of the condition.
In conclusion, differential diagnosis plays a critical role in accurately diagnosing cervical spondylosis and ruling out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience neck pain or stiffness as early intervention can improve outcomes.
Cervical spondylosis headache is a common symptom. Pain is usually due to arthritic motion of cervical vertebrae. Frequently there is an overlap in the type of doctors who will treat neck and head pain from cervical spondylosis. Cervical spondylosis commonly cause headache, especially in the back part of the head (Occipitalgia). Best doctor for cervical pain is usually a spine surgeon who treats problems related to neck and back pain. However, a general orthopedic surgeon also can be consulted. If your symptoms are primarily headache, then it is better to consult a neurologist, who deals with brain and related disorders. A neurologist will also be able to give primary treatment for mild cervical spondylosis causing neck and head pain. However, for severe cervical spondylosis, they will refer the patient to a spine surgeon.
Yes. Cervical spondylosis or cervical spondylitis denote same condition. Spond= vertebra, osis/ itis= inflammation. Thats means inflammation of cervical vertebral joints due to chronic wear and tear of the body.
Spine surgeons are best doctor for cervical pain; however, patients can also consult an orthopedic surgeon, neurologist or neurosurgeon near their locality. Initial treatment for cervical pain is usually symptomatic treatment, which can be given by even a family physician and the patient doesn’t necessarily need to see a specialist doctor for cervical spondylosis.
In following situations patients should see a spondylosis specialist doctor near their locality:
- symptoms not resolving with medical treatments,
- Severe symptoms,
- Presence of neurological compression, e.g. tingling-numbness, loss of sensation or weakness in arms/ legs.
- Any history of trauma, high fever, sudden loss of weight, or any other associated severe symptoms.
Cervical spondylosis is essentially wear and tear of vertebral joints between cervical vertebrae. Intervertebral disc and facet joints are primarily affected. Cartilage of these joints gets arthritic which is called spondylosis. In addition there is osteophyte formation. Osteophytes are overgrown bones at the margin of the vertebral bodies. This is body’s natural mechanism to stabilize the arthritic joint to prevent motion causing pain.
C4-5 and C5-6 cervical joints are in the middle of cervical spine. These joints are subjected to maximum movement stress. This leads to C4-5 and C5-6 spondylosis being most common. However, C3-4 and C6-7 spondylosis is also not uncommon.